Ever wondered who decides what makes a high visibility safety vest safe enough for the job? When workers’ lives depend on being seen, clear standards for high visibility apparel are critical. This article dives into the organizations behind these specifications, explaining their roles, key standards, and how they ensure safety across industries like construction, roadwork, and logistics. You’ll learn about global and regional regulations, specific requirements like reflective stripes, and why compliance matters for your workforce. Let’s explore the frameworks that keep safety first.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are High Visibility Safety Vest Standards?
High visibility safety vest standards define the design, materials, and performance requirements for apparel that ensures workers are visible in low-light or high-risk environments. These standards, set by authoritative organizations, cover elements like color, reflectivity, and durability. Why do they matter? They reduce accidents by ensuring vests meet strict safety criteria. For example, standards dictate the placement of reflective stripes and the fluorescence of fabrics, critical for workers in construction or traffic management.

ANSI/ISEA 107: The U.S. Standard for High Visibility Apparel
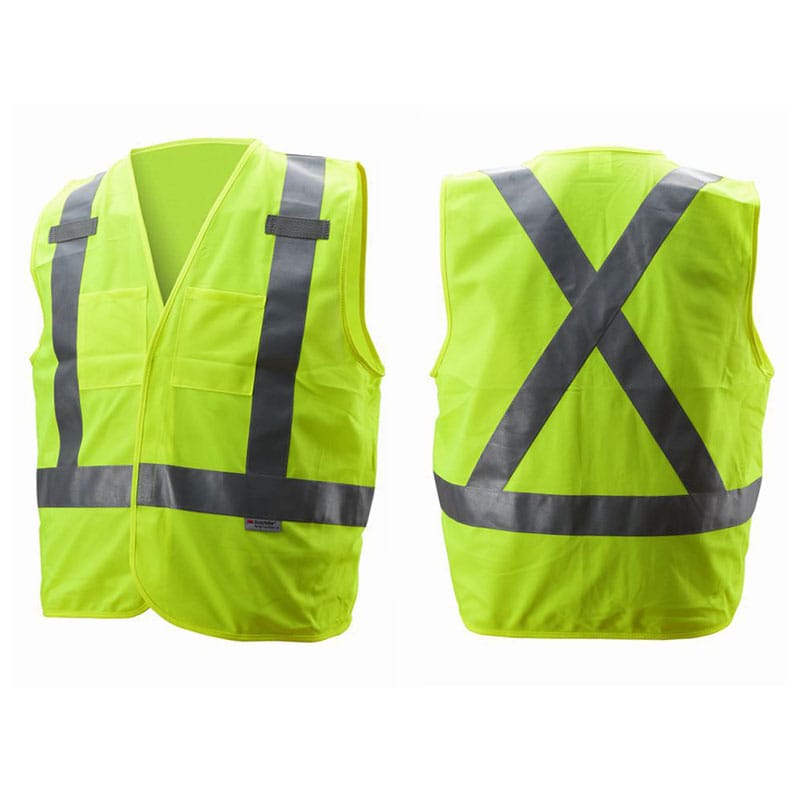
In the United States, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Safety Equipment Association (ISEA) developed ANSI/ISEA 107, the go-to standard for high visibility safety vests. This standard classifies apparel into three types—Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3—based on the level of visibility needed. For instance, safety vests with pockets Class 3 offer the highest visibility, requiring more reflective material for high-risk environments like highways. The standard specifies fluorescent colors (yellow-green, orange-red, or red) and mandates at least 200 square inches of reflective tape for Class 2 vests.
ANSI/ISEA 107 also addresses performance criteria, such as colorfastness and tear resistance, ensuring vests withstand harsh conditions. Compliance is voluntary but widely adopted, as many employers, including those in construction, prioritize certified gear to meet OSHA requirements. Curious about Class 3 vests? They’re designed for maximum visibility, often used by workers exposed to high-speed traffic.

EN ISO 20471: The European Benchmark for Visibility
Across the Atlantic, EN ISO 20471 is the European standard for high visibility clothing, set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Similar to ANSI/ISEA 107, it categorizes apparel into three classes based on reflective material and fluorescent fabric area. A safety vest with reflective stripe compliant with EN ISO 20471 Class 2, for example, requires at least 0.5 square meters of fluorescent material and 0.13 square meters of reflective tape. This standard is mandatory in many European countries for workers in high-risk settings like road construction.
EN ISO 20471 emphasizes durability, requiring vests to maintain visibility after repeated washing. It’s stricter than ANSI in some respects, particularly for color retention. If you’re sourcing vests for European markets, compliance with this standard is non-negotiable. It ensures workers remain visible, reducing risks in foggy or dark conditions.

VicRoads and Australian Standards for Hi Vis Vests
In Australia, VicRoads, the state road authority in Victoria, plays a key role in setting requirements for high visibility apparel, particularly for road workers. A VicRoads approved hi vis vest must comply with AS/NZS 4602.1, the Australian/New Zealand standard for high visibility safety garments. This standard outlines requirements for daytime and nighttime visibility, specifying colors like fluorescent yellow or orange and retroreflective materials for low-light conditions.
AS/NZS 4602.1 is tailored to Australia’s unique environments, such as intense sunlight, which affects color perception. Vests must maintain visibility after UV exposure, a critical factor for outdoor workers. If your team operates in Victoria, sourcing VicRoads approved hi vis vests ensures compliance with local regulations and enhances worker safety.

Flame-Resistant Hi Vis Vests: NFPA 2112 and Beyond
For workers in industries like oil and gas, flame-resistant (FR) high visibility vests are critical. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets standards like NFPA 2112, which focuses on flame-resistant garments. An FR hi vis vest must meet both NFPA 2112 for fire resistance and ANSI/ISEA 107 or EN ISO 20471 for visibility. These vests use specialized fabrics that self-extinguish when exposed to flames, protecting workers in high-risk settings like refineries.
Why combine FR and hi vis standards? Workers in hazardous environments need protection from multiple risks—fire and low visibility. NFPA 2112 ensures the vest won’t ignite, while visibility standards guarantee workers are seen. Procurement managers sourcing FR hi vis vests should verify dual certification to meet regulatory and safety needs.

OSHA’s Role in High Visibility Apparel
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. doesn’t create specific high visibility standards but enforces their use through regulations like 29 CFR 1926.651 for construction. OSHA often references ANSI/ISEA 107, requiring high visibility safety vests in environments like roadwork or warehouses. For example, workers exposed to vehicle traffic must wear Class 2 or Class 3 vests, depending on the risk level.
OSHA’s guidelines emphasize risk assessment. If your workplace involves moving equipment or low-light conditions, compliance with high visibility standards isn’t just a suggestion—it’s a mandate. Non-compliance can lead to fines or, worse, accidents. Checking OSHA’s requirements helps ensure your vests meet federal expectations.

Other Global Standards for High Visibility Apparel
Beyond the U.S., Europe, and Australia, other regions have their own standards. In Canada, CSA Z96 governs high visibility safety apparel, similar to ANSI/ISEA 107 but with adjustments for colder climates. In Japan, JIS T 8127 sets requirements for high visibility clothing, focusing on urban environments. These standards share common goals: bright colors, reflective materials, and durability.
For global businesses, understanding these variations is key. A high visibility safety vest compliant in one country may not meet another’s requirements. Always check local regulations when sourcing vests for international teams.
Comparison Table: Global High Visibility Standards
| Standard | Region | Key Features | Class Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANSI/ISEA 107 | USA | Fluorescent colors, reflective tape area | 1, 2, 3 |
| EN ISO 20471 | Europe | Strict color retention, wash durability | 1, 2, 3 |
| AS/NZS 4602.1 | Australia/NZ | UV resistance, day/night visibility | Day, Night |
| CSA Z96 | Canada | Cold-weather durability, reflective bands | 1, 2, 3 |
| JIS T 8127 | Japan | Urban-focused, high reflectivity | 1, 2, 3 |

Why Compliance with High Visibility Standards Matters
Compliance isn’t just about checking boxes—it saves lives. High visibility safety vest standards ensure workers are seen in dangerous conditions, reducing the risk of collisions or accidents. For businesses, adhering to standards like ANSI/ISEA 107 or EN ISO 20471 builds trust with employees and regulators. Non-compliant vests can lead to legal issues or workplace injuries, costing more than just fines.
Consider a construction site at dusk: a worker in a Class 3 vest with reflective stripes is far more visible than one in a non-compliant vest. Investing in certified apparel shows you prioritize safety and reliability.

Choosing the Right High Visibility Vest for Your Needs
Selecting the right vest depends on your industry and regulatory requirements. For roadwork, a VicRoads approved hi vis vest ensures compliance in Australia. For oil and gas, an FR hi vis vest meeting NFPA 2112 is essential. Consider factors like visibility class, pocket functionality (e.g., safety vests with pockets Class 3), and environmental conditions. Always verify certifications with suppliers to avoid substandard products.
Need help navigating these standards? A trusted manufacturer like Yolite can provide vests tailored to your region and industry, ensuring compliance and safety.

Frequently Asked Questions
ANSI/ISEA, ISO, and regional bodies like VicRoads establish standards like ANSI/ISEA 107, EN ISO 20471, and AS/NZS 4602.1. These ensure vests meet visibility and durability requirements. Contact us for compliant vest options.
Reflective stripes enhance visibility in low-light conditions, as required by standards like EN ISO 20471. They reflect light from vehicles, reducing accident risks. Ask us about vests with optimal reflective designs.
Class 3 safety vests offer the highest visibility, with extensive reflective material for high-risk settings. Pockets add functionality for tools. We can supply Class 3 vests meeting ANSI/ISEA 107.
FR hi vis vests are critical for industries like oil and gas, where fire risks are high. They meet NFPA 2112 and visibility standards. Request samples to evaluate FR vests for your team.
VicRoads approved vests comply with AS/NZS 4602.1, designed for Australian conditions like UV exposure. They ensure visibility for road workers. Contact us to source compliant vests for Victoria.
To verify a high visibility safety vest’s compliance, check for certification labels or documentation from standards like ANSI/ISEA 107, EN ISO 20471, or AS/NZS 4602.1. Request test reports or compliance certificates from the manufacturer. Reputable suppliers, like Yolite, provide vests with clear labeling and documentation to ensure adherence to global standards. Contact us for detailed certification information or samples.
Ready to ensure your workforce stays safe and compliant? As a direct manufacturer, Yolite offers high visibility safety vests tailored to global standards, from ANSI/ISEA 107 to EN ISO 20471. Whether you need Class 3 vests with pockets or flame-resistant options, we’ve got you covered. Contact us today to request samples or discuss your specific needs—let’s keep safety first.